In our rapidly changing world, the effects of climate change are becoming increasingly evident. As businesses and governments strive to reduce their impact on the environment, tools such as the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol have become essential for tracking and managing greenhouse gas emissions. The GHG Protocol plays a pivotal role in helping organisations align their emission reduction efforts with global climate goals, including those set by the Paris Climate Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2°C, with efforts to limit it to 1.5°C.
In this blog, we will explore:
- What is the GHG Protocol?
- Why is the GHG Protocol Important?
- Core Principles of the GHG Protocol for Effective Emissions Reporting
- Future Implications of GHG Protocol
- How sentra.world helps in GHG Calculations?
What is the GHG Protocol?
The GHG Protocol is a widely recognized accounting tool developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) to help organizations and governments measure, manage, and report greenhouse gas emissions. It provides a standardized framework for calculating emissions from a variety of sources, including electricity consumption, transportation, and industrial processes. By using the GHG Protocol, entities can better understand their carbon footprint and identify opportunities for emissions reductions.
Why is the GHG Protocol Important?
With global temperatures rising and climate-related disasters becoming more frequent, such as the severe flooding in Kerala in 2018 and the heatwaves across North India, there is an urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The GHG Protocol plays a crucial role by providing a consistent and transparent methodology for measuring emissions. This allows organizations to set emission reduction targets, track progress over time, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability to stakeholders.
Additionally, the GHG Protocol helps facilitate international cooperation on climate action by providing a common language for reporting emissions. This standardization is essential for comparing emissions data across organizations and countries, enabling better-informed decision-making and policy development.
Core Principles of the GHG Protocol for Effective Emissions Reporting
The GHG Protocol is guided by five key principles: Relevance, ensuring the GHG inventory reflects the company’s emissions profile; Completeness, covering all emission sources within the boundary; Consistency, enabling meaningful comparisons over time; Transparency, with clear documentation of methodologies and assumptions; and Accuracy, ensuring reliable data without material misstatements. These principles provide a robust framework for accurate and consistent GHG accounting, essential for effective climate change strategies and reporting.
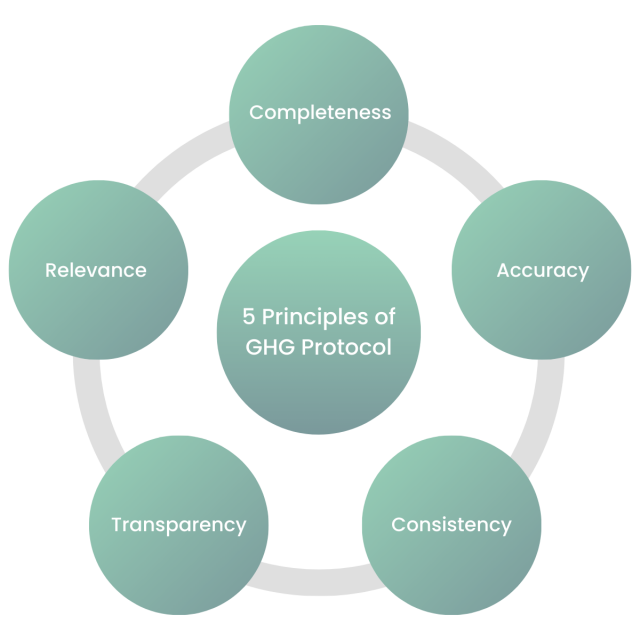
Current Values of the GHG Protocol
Since its inception in 1998, the GHG Protocol has become the most widely used accounting standard for greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. Thousands of organizations, including businesses, governments, and non-profit organisations, have adopted the GHG Protocol to measure and manage their emissions.
While the GHG Protocol is universally applicable, it recognizes that one size doesn’t fit all when it comes to emission reporting. That’s why it offers a range of different standards, each designed to meet the specific needs of organizations as per the situation. Let’s understand it in simple terms:
- Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard
- Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Standard
- GHG Protocol for Project Accounting
- Product Life Cycle Standard
- City and Community-Scale GHG Emissions Protocol
- GHG Protocol for Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use (AFOLU)
Future Implications of the GHG Protocol
Looking ahead, the GHG Protocol will continue to play a key role in the global transition to a low-carbon economy. As countries implement more ambitious climate targets under the Paris Agreement, the demand for robust emissions accounting tools like the GHG Protocol will only increase.
In particular, the GHG Protocol is expected to evolve to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the transition to a sustainable future. This may include updates to reflect new scientific findings, changes in regulatory requirements, and advancements in technologies for measuring and reducing emissions.
Furthermore, the GHG Protocol is likely to become even more integrated with other sustainability frameworks, such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). This cross-pollination of reporting standards will enable organizations to better align their climate goals with broader sustainability objectives and financial risk management.
How sentra.world help in GHG Calculations?
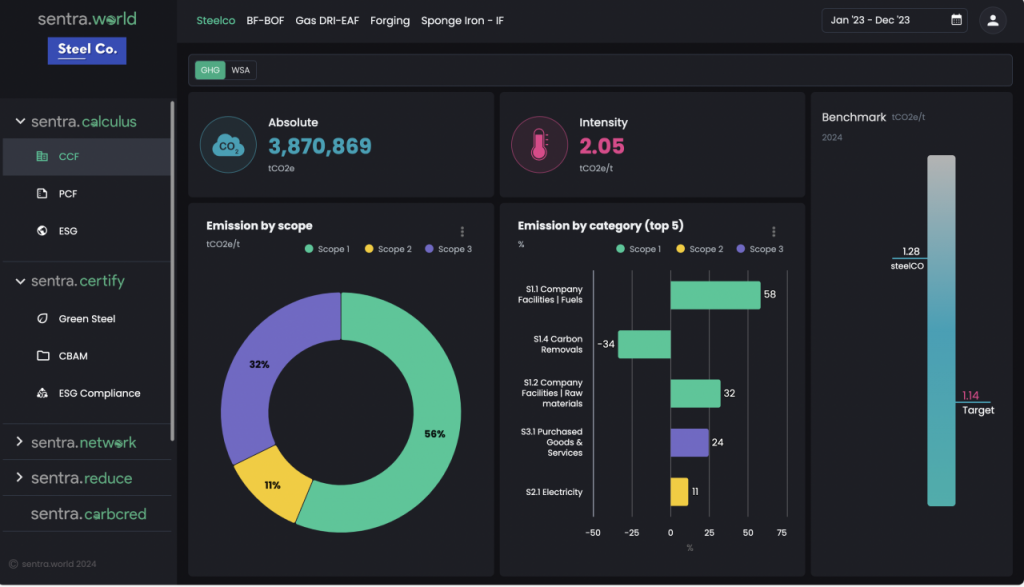
sentra.world can play a pivotal role in supporting organizations in implementing the GHG Protocol by offering innovative solutions for greenhouse gas accounting and reporting. Through advanced data analytics, automation, and integrated platforms, sentra.world can streamline the process of tracking emissions across different scopes (1, 2, and 3), making it easier for businesses to monitor their carbon footprint and identify reduction opportunities. By providing real-time insights and comprehensive reports, sentra.world can enable organizations to not only comply with global standards but also drive meaningful progress toward their sustainability and climate goals. This contribution can further enhance transparency, foster accountability, and promote collaboration in the fight against climate change.
In conclusion, the GHG Protocol is a critical tool for organizations and governments seeking to address climate change and contribute to a more sustainable future. By accurately measuring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions, entities can take informed actions to reduce their impact on the environment and build resilience in the face of climate risks. As we look towards the future, the GHG Protocol will continue to be a guiding light in the transition to a low-carbon, resilient economy.

