The emergence of the Green Steel Taxonomy for India marks a pivotal moment in the global steel industry, particularly as nations strive to meet ambitious climate goals. Launched by India on December 12, 2024, this groundbreaking initiative aims to decarbonise the steel sector, which is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. With a clear framework for defining and categorizing green steel based on its carbon emissions, India becomes the first country to establish such a taxonomy, setting a precedent for sustainable practices worldwide. The industrial revolution brought many advancements but also caused significant harm to the environment. Steel production is one of the biggest contributors to carbon emissions, accounting for about 7-9% of global greenhouse gases. To combat this, “Green Steel” has become a key solution for reducing the impact of steelmaking on the planet. But what is Green Steel, and how can we measure its environmental benefits? This is where the Green Steel Taxonomy for India comes in.
In this blog, we will explore:
- Understanding Green Steel Type
- Taxonomy of Green Steel — Understanding Ratings
- The Role of NISST in Green Steel Certification
- Certification Process
- Emissions Scope and Methodology
- Why Green Steel Matters?
- Importance of Certification in Green Steel
- Conclusion
Understanding Green Steel
Green Steel refers to steel that is manufactured with reduced carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to conventional methods. This is achieved through innovations like using hydrogen instead of coke as a reducing agent, integrating renewable energy sources in production, or recycling scrap steel. For instance, producing one ton of green steel can reduce carbon emissions by about 70% compared to traditional methods. The ultimate goal is to minimize the carbon footprint per tonne of finished steel (tfs), paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Taxonomy of Green Steel — Understanding Ratings
Recognizing the environmental significance of green steel, India is taking Bold Steps Towards a Sustainable Steel Future with transformative initiatives reshaping the industry. Taxonomies classify green steel products based on their sustainability credentials, incorporating metrics such as carbon emissions and resource efficiency. For example, Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) offer a standardized framework to convey the environmental impact of products, with higher ratings indicating superior sustainability performance. This allows manufacturers to effectively market their green steel products while providing clarity and transparency for consumers who are increasingly choosing environmentally responsible products. Rating systems typically evaluate the entire lifecycle of the steel, from raw material extraction to the final product. With a clear taxonomy in place, stakeholders can make informed purchasing decisions grounded in sustainability. Here’s how it works:
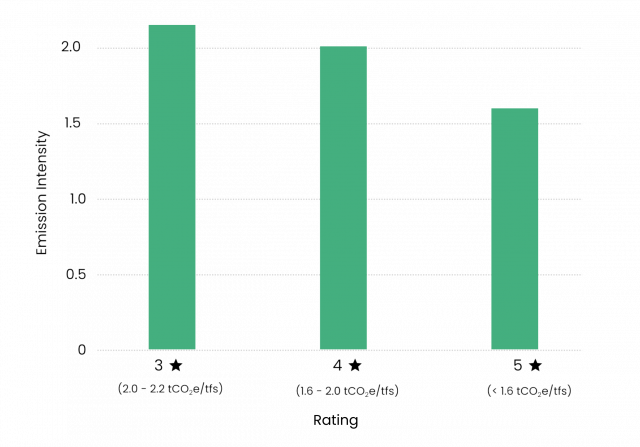
Based on the greenness percentage, the taxonomy categorizes steel into different star ratings:
- Five-Star Green-Rated Steel: Emission intensity below 1.6 t-CO2e/tfs.
- Four-Star Green-Rated Steel: Emission intensity between 1.6 and 2.0 t-CO2e/tfs.
- Three-Star Green-Rated Steel: Emission intensity between 2.0 and 2.2 t-CO2e/tfs.
Steel with an emission intensity higher than 2.2 t-CO2e/tfs is not eligible for a green rating. This rating system provides transparency and incentivizes manufacturers to adopt cleaner technologies.
To know more about Green Steel Taxonomy for India, check out our exclusive webinar recording on “Mastering Green Steel Taxonomy & CCTS” conducted with expects and government officials, from here.
The Role of NISST in Green Steel Certification
The National Institute of Secondary Steel Technology (NISST) plays a pivotal role in the implementation and oversight of India’s Green Steel Taxonomy, which was launched on December 12, 2024. As the designated nodal agency, NISST is tasked with several critical functions that are essential for the successful adoption of this groundbreaking framework aimed at decarbonising the steel industry.
The National Institute of Secondary Steel Technology is vital in promoting green steel initiatives. Its responsibilities include:
- Measurement, Reporting, and Verification (MRV): Ensuring accurate data on emissions.
- Certification Issuance: Awarding greenness certificates and star ratings.
- Registry Maintenance: Keeping a record of green-rated steel plants and their outputs.
NISST’s efforts align closely with India’s broader climate goals, particularly the National Mission on Green Steel, which aims to achieve net-zero emissions in the steel sector by 2070. By facilitating a clear framework for evaluating and certifying green steel, NISST not only supports environmental sustainability but also enhances India’s competitiveness in global markets increasingly focused on sustainability.
Certification Process
Steel plants seeking certification must register with NISST. The process involves the following steps:
- Registration Fee: A one-time amount of Rs. 10,000 is charged per steel plant.
- Certification Fee: On every 500 tonnes of finished steel certified, Rs. 1,000 will be charged.
- Validity: Certificates are issued annually, with provisions for mid-year updates if MRV data changes.
The certification details include:
- Plant name
- Embodied emissions at the finished steel level
- Greenness percentage
- Star rating
- Certified quantity
Emissions Scope and Methodology
The emissions scope for green steel certification includes:
- Scope 1: Direct emissions from on-site activities.
- Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased electricity.
- Limited Scope 3: Emissions from activities such as sintering, pellet making, and coke production. Upstream and downstream emissions are excluded for simplicity.
Why Green Steel Matters?
As the world races against time to mitigate climate change, the decarbonisation of hard-to-abate sectors like steel production becomes imperative. Green Steel offers multiple benefits, including:
- Reduced Emissions: Green steel plays a direct role in reducing global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. By using advanced technologies and eco-friendly processes, such as hydrogen-based steel production or recycling, green steel manufacturing helps lower the overall carbon footprint of the steel industry. This reduction contributes significantly to global efforts to combat climate change and supports achieving net-zero emissions goals.
- Economic Opportunity: The demand for green building certifications is rising rapidly, driven by builders and industries like IT that prioritize sustainable infrastructure. Green buildings offer significant advantages, including up to 15% higher rental income, making them attractive to builders. For IT organizations, such spaces help them achieve their sustainability targets, such as those aligned with 2030 goals. This increasing demand for green-certified buildings also fuels the need for green steel products, as they are a key component of achieving such certifications. Certifications like EPD, IGBC Green Building Certification, and Green Pro Certification further enhance the adoption of green steel in sustainable construction.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adopting green steel ensures compliance with international environmental regulations and agreements, such as the Paris Agreement. Many governments and trade bodies are implementing mechanisms like the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which imposes carbon tariffs on imports from countries with lax environmental standards. Green steel production aligns with these frameworks, helping industries avoid penalties and ensuring smoother trade across global markets. Moreover the government has stated that for the upcoming projects government will only use green steel, in order to build green projects.
- Future-Ready Infrastructure: As the world transitions to a low-carbon economy, steel plants need to adopt sustainable practices to remain competitive. Green steel equips industries with future-ready infrastructure by integrating low-carbon technologies, reducing dependency on fossil fuels, and meeting evolving consumer and regulatory expectations. This readiness ensures that steel plants stay relevant and thrive in a rapidly transforming market landscape focused on sustainability.
Importance of Certification in Green Steel
The certification of green steel is a crucial element in the transition towards more sustainable manufacturing practices within the steel industry. With the launch of India’s Green Steel Taxonomy, this certification not only provides a framework for evaluating and categorising steel products based on their environmental impact but also serves multiple significant purposes that benefit manufacturers, consumers, and the environment alike. A reputable certification reassures consumers and businesses of the manufacturers’ environmental claims. It builds trust and clarity in a market that increasingly favours sustainable options.
Furthermore, NISST certification helps enhance a company’s reputation, potentially increasing its market presence as more consumers seek green alternatives. Compliance with recognized sustainability standards can also provide competitive advantages as regulatory pressures tighten globally.
Conclusion
The Green Steel Taxonomy offers a structured framework to assess and promote sustainable practices in the steel industry. By categorizing and certifying steel based on emission intensity, it fosters accountability and incentivizes progress. As the world grapples with climate change, such initiatives play a pivotal role in reducing industrial emissions and achieving global decarbonisation goals. The journey toward green steel is challenging but indispensable. By embracing this taxonomy, stakeholders across the value chain—from manufacturers to consumers—can contribute to a sustainable future.
Both manufacturers and consumers can engage in the shift toward a more sustainable future. At sentra.world, we help industries measure and mitigate carbon emissions. By proactively addressing their carbon footprint, companies not only contribute to global climate goals but also secure a sustainable and resilient future for their business and stakeholders. Partnering with sentra.world will not just help companies get an accurate baseline view of their corporate carbon footprint but also facilitate effective charting out of decarbonization pathways.
Embracing these principles not only supports environmental goals but also nurtures a culture that prioritizes sustainability in production.


